Good Overall Health is Linked to the Function of the Glycocalyx
The endothelial glycocalyx is defined as a vast protective micro-thin gel lining of all capillaries that touch each of the trillions of cells. The integrity of the glycocalyx structure and function is important because the continuous delivery of nutrients and hormones, and the elimination of waste, flows through the capillaries.
When glycocalyx function becomes compromised due to aging, poor diet, lack of exercise, genetics, stress, and other factors, it can become leaky. And when that happens, diseases and conditions can silently begin. Organs begin to starve without vital nutrients delivered through the capillaries and glycocalyx, leading to health decline.
Every cell of the body is nourished by the blood that travels through the capillaries that make up 99% of the circulatory system from head to toe.
Placed end-to-end, scientists estimate they would extend 60,000 miles, enough to go around the earth two-and-a-half times. With every heartbeat, vital nutrients and oxygen are delivered and waste is removed from each cell. This essential function breaks down with aging, poor diet, lack of exercise, genetics, stress, and smoking.
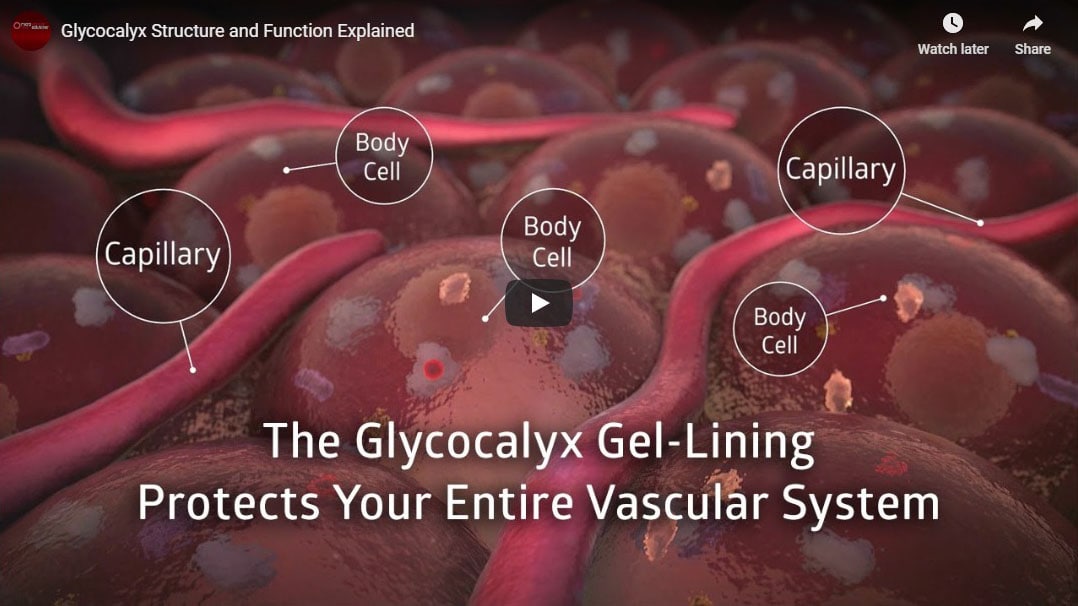
New medical science reveals the importance of the healthy structure of the glycocalyx that protects the entire circulatory system.
In the past, blood vessels were thought to be simple hollow tubes. But with today’s high-resolution video microscopes, a discovery reveals that the entire circulatory system is coated with a gel-like lining that protects the inside walls of the arteries, veins, and capillaries.
The glycocalyx keeps the body healthy in three critical ways.

First, it functions as the natural trigger that stimulates the production of nitric oxide. Nitric oxide is vital in controlling blood flow and blood pressure. The glycocalyx stores antioxidants and, working together with nitric oxide, both increase blood flow, on demand, when organs call for it. For example, when walking upstairs. Or even when the brain is working through a difficult problem. Bottom line: the body needs a thick and healthy glycocalyx to efficiently regulate blood flow.

Second, glycocalyx structure allows the body to engage more of the available capillaries of the microvascular system when blood flow increases. This is critical to regulate the supply of nutrients and oxygen, and the removal of waste and carbon dioxide, according to the body’s level of activity, such as when exercising. Bottom line: While blood flow control is important, the glycocalyx allows the body to engage more capillaries when organs demand nourishment and waste removal.

Third, capillaries are much more than simple hollow tubes. In fact, their inner surface is coated with the non-stick glycocalyx that prevents loss of capillaries through fluid leakage, blood clotting and inflammation. This coating prevents sticking when unneeded, and it keeps blood clotting and inflammation under control. For example, when the body is healthy, it can repair a simple cut or fight an infection. Bottom line: a healthy glycocalyx not only engages more capillaries when blood flow goes up, but it also protects the capillary network and even the entire vascular system from deterioration and loss.